Mined from metamorphic and igneous rock, it varies considerably in crystallinity. Read More…
At Weaver Industries we specialize in manufacturing machined graphite parts and products. Our goal is to ensure that our customers get the right tools for their applications. We are leaders in the industry for our graphite machining processes which include recycling and reclaiming machined electrodes. Custom molded urethane and high quality carbon graphite are only a few of our other...

At Amsted, we specialize in precision graphite machining, delivering advanced solutions that meet the exacting standards of modern industries. Our team brings together decades of expertise and state-of-the-art technology to produce high-performance graphite components with superior accuracy, consistency, and surface quality.
SGL Carbon Group is the world's largest manufacturer of carbon and graphite, a leading provider of graphite specialties and the only company in the world to master all related manufacturing processes. We serve many industries with graphite materials, system solutions and graphite design.

More Graphite Material Companies
Natural graphite remains stable over a wide range of temperatures, making it an excellent conductor of heat and electricity. With a melting point of 3650°C (6602°F), it has a wide array of applications in machining. Natural graphite is further divided into three material subcategories: amorphous, flake and high crystalline.
This mineral is most frequently used for refractories, batteries, steelmaking, expanded graphite, brake linings, foundry facings and lubricants. Synthetic graphite can made using coke and pitch. Synthetic graphite typically has a higher purity than naturally occurring graphite, but is not as crystalline as natural graphite. Also, synthetic graphite generally has a lower density, higher porosity, and higher electrical resistance. Because of its porosity level, this type of graphite should not be used for refractory applications.
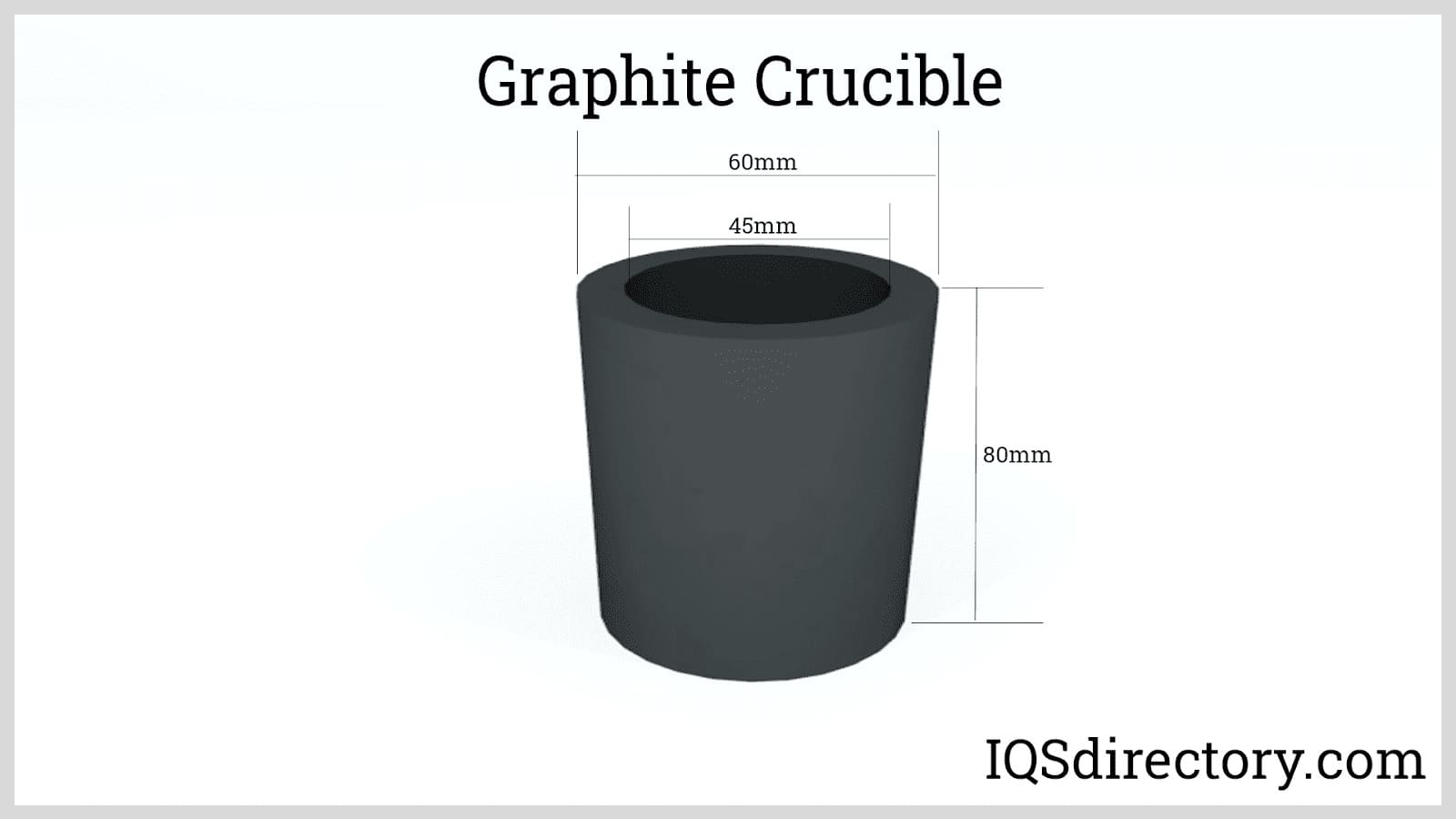
Graphite can be used for refractory materials, as mentioned, but it also has many applications in the electrical, chemical, nuclear and mechanical industries. In the refractory world, graphite is used to build kiln and blast furnace bricks. It is also used to produce crucibles, ladles and moulds for holding molten metals. Graphite flake is one of the most commonly used materials in the manufacturing of refractories made for the continuous casting of steel. In the electrical world, graphite's main use is in making carbon brushes and electric motors.
Graphite also works well in the chemical industry because of its extremely high melting point. It is used in such high-temperature processes as the production of phosphorus and calcium carbide in arc furnaces. It is also used to conduct electricity in some aqueous electrolytic processes like the production of halogens like chlorine and fluorine.
High purity electrographite is well-suited to the nuclear industry because of its low absorption of neutrons, high thermal conductivity and ability to maintain strength at high temperatures. It is used in large amounts in the production of moderator rods and reflector components in nuclear reactors. Graphite is largely used in the world of mechanics and engineering.
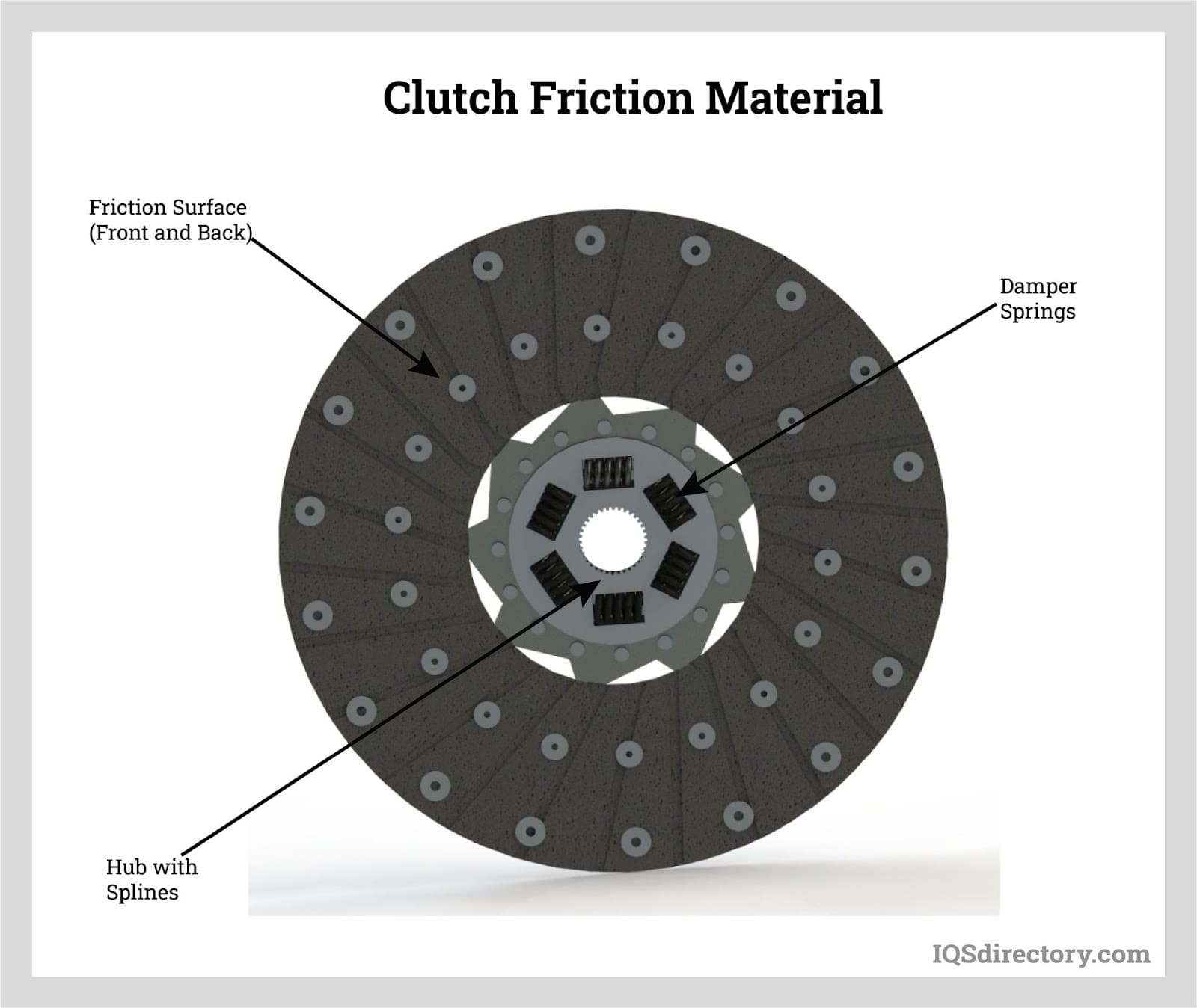
Applications include piston rings, thrust bearings, journal bearings and vanes. Additionally, graphite-derived carbon based seals are used widely in the shafts and fuel pumps of aircraft jet engines.
Some types of graphite are better suited to certain applications than others, though they often overlap to some degree or another. For example, amorphous graphite is well-suited to metallurgy, pencil production, refractories, coatings, lubricants and paint production. Flake graphite, while also used for refractories, is predominantly used for secondary steel production. It is sometimes also used in lubricants, powder metallurgy, pencils and coatings.
Crystalline graphite is mostly used in batteries and grinding wheels, though it can also be used in lubricants and powder metallurgy. All forms of natural graphite are used in the production of graphite foil. Synthetic graphite is also used in batteries, but unlike natural graphite, is further used in aerospace applications, carbon brushes, graphite electrodes and moderator rods in nuclear power plants.






 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services