Graphite machining is the process of cutting or shaping graphite material into a desired shape or size. Graphite is a form of carbon that is highly conductive and chemically stable, making it a popular material for a wide range of applications. Graphite machining involves specialized tools and processes that are designed to produce high-quality, precision components with a range of complex geometries. Read More…
At Weaver Industries we specialize in manufacturing machined graphite parts and products. Our goal is to ensure that our customers get the right tools for their applications. We are leaders in the industry for our graphite machining processes which include recycling and reclaiming machined electrodes. Custom molded urethane and high quality carbon graphite are only a few of our other...

At Amsted, we specialize in precision graphite machining, delivering advanced solutions that meet the exacting standards of modern industries. Our team brings together decades of expertise and state-of-the-art technology to produce high-performance graphite components with superior accuracy, consistency, and surface quality.
SGL Carbon Group is the world's largest manufacturer of carbon and graphite, a leading provider of graphite specialties and the only company in the world to master all related manufacturing processes. We serve many industries with graphite materials, system solutions and graphite design.

More Graphite Machining Companies
For centuries, graphite has served as a valuable material, primarily utilized as both a lubricant and a medium for drawing. However, it was not until the 1800s that its potential for industrial applications began to be realized. The early 1900s marked a significant turning point with the burgeoning electrical industry, which spurred a heightened demand for graphite products. This era saw the advent of graphite machining as a distinct and specialized field, catalyzing advancements and broadening the scope of graphite’s utility in various technological and industrial sectors.

What Is Graphite Machining?
Graphite machining refers to the precision manufacturing process of shaping, cutting, and finishing graphite materials into desired components or products. This specialized process leverages the unique properties of graphite, such as high thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability, to produce parts for demanding industrial applications. As industries seek materials that withstand extreme environments and offer long service life, graphite machining has become a critical solution, especially in the production of graphite molds, electrodes, dies, crucibles, and other custom graphite products.
Why Choose Graphite Machining? Exploring Buyer Intent and Applications
Are you searching for robust, high-performance materials for your next industrial project? Do you need custom components with tight tolerances and exceptional durability? Graphite machining delivers solutions for a wide range of buyer intent scenarios, from sourcing raw graphite blocks for prototyping to fully finished, application-ready graphite components for OEMs and end-users. Companies invest in graphite machining services to benefit from:
- Superior Heat Resistance: Machined graphite parts maintain stability and integrity at temperatures exceeding 3000°C, making them ideal for high-heat applications.
- Electrical Conductivity: Graphite electrodes and connectors are essential in electrical discharge machining (EDM), arc furnaces, and battery manufacturing.
- Chemical Inertness: Graphite components resist acids, alkalis, and corrosion, which is essential for chemical processing, metallurgy, and laboratory equipment.
- Precision Manufacturing: CNC graphite machining achieves intricate designs and complex geometries with tight tolerances, suitable for semiconductor, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing sectors.
- Lightweight and Durable: Machined graphite offers high strength-to-weight ratio, reducing system weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Graphite Machining Equipment
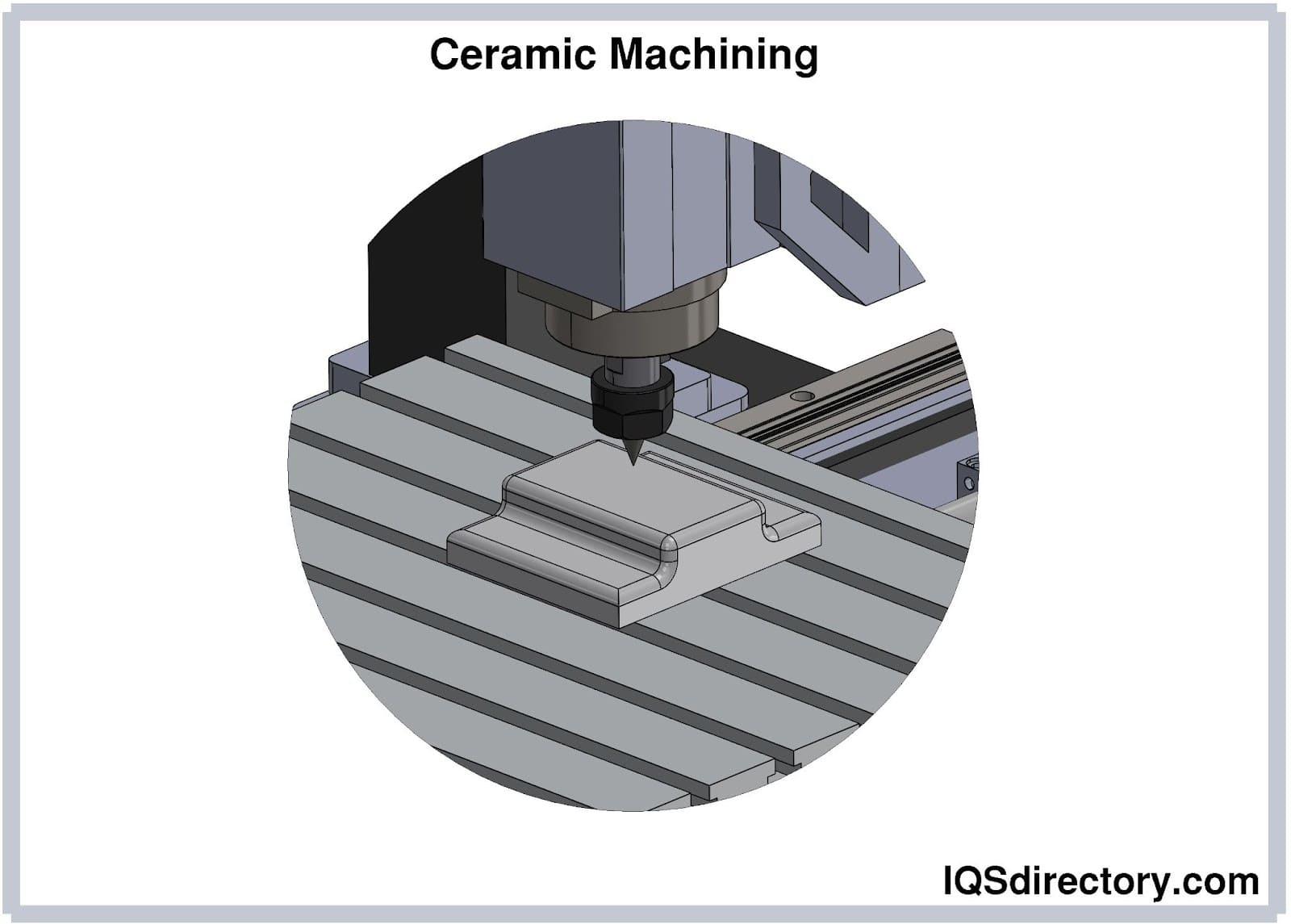
Graphite machining is a sophisticated process that necessitates the use of specialized equipment to manage the unique properties of graphite. This material, known for its brittleness and susceptibility to chipping or cracking, demands machinery that can handle its delicate nature. Typically, high-speed milling machines, CNC (computer numerical control) machines, and EDM (electrical discharge machining) machines are employed to achieve the precise shaping and detailing required.
The selection and maintenance of tools used in graphite machining are equally crucial to ensure both quality and accuracy. Cutting tools designed specifically for graphite are crafted from high-quality materials capable of withstanding the substantial temperatures and pressures encountered during the machining process. These tools must be meticulously maintained and sharpened to avoid any chipping or breakage, which can compromise the integrity of the machined graphite. CNC machines play a vital role in this realm, offering unparalleled precision and accuracy, which are essential for producing intricate and reliable graphite components.
Common Graphite Machining Tools and Technologies
- CNC Milling Machines: Capable of 3-axis and 5-axis machining, CNC mills deliver high-speed, high-precision cutting for complex parts.
- EDM Machines: Electrical Discharge Machining is used for fine detail work, particularly in mold and die manufacturing, ensuring consistency and definition for intricate shapes.
- Diamond-Coated Tooling: Diamond-coated end mills, drills, and lathes reduce tool wear and increase productivity when working with abrasive graphite materials.
- Dust Collection Systems: Essential for capturing hazardous graphite dust, protecting operator health, and maintaining a clean production environment.
- Advanced Inspection Tools: CMMs (coordinate measuring machines) and optical scanners verify dimensional accuracy of finished graphite components.
Are you evaluating which graphite machining equipment best meets your production needs? Consider factors such as part complexity, required tolerances, production volume, and environmental controls for dust and debris.
Graphite Machining Processes
Graphite machining primarily involves the milling process, renowned for its efficiency and precision. Milling is complemented by other essential techniques such as turning, drilling, and grinding, each bringing its unique strengths to the table. For more intricate or complex shapes, Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is frequently employed due to its ability to achieve fine detail and precision.
Each of these machining processes offers specific advantages and disadvantages, making the choice of method highly dependent on the particular requirements of the application at hand. The selection process involves a careful evaluation of the desired outcome, material properties, and the complexity of the design. Below, we delve into the distinctive characteristics and applications of these graphite machining processes, highlighting their unique contributions to the field.
Milling: stands as the most prevalent process in graphite machining. This technique employs a rotating cutting tool, such as an end mill or a face mill, to meticulously remove material from the graphite’s surface. Milling excels in producing flat or contoured surfaces, along with intricate pockets or slots, making it indispensable for detailed and precise work.
Turning:, on the other hand, utilizes a lathe to rotate the graphite while a cutting tool removes material from its surface. This method is particularly suited for crafting cylindrical shapes, such as rods or tubes, ensuring uniformity and precision in the final product.
Drilling: in graphite machining involves the use of a rotating cutting tool, like a drill bit, to create precise holes. This process is essential for producing holes for fasteners or creating openings for various components, ensuring accurate and reliable fittings in assembled structures.
Grinding: employs an abrasive wheel to remove material from the graphite’s surface, achieving exceptionally smooth and flat finishes. This process is ideal for applications requiring very tight tolerances, ensuring the highest standards of precision and surface quality.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): is a sophisticated technique that utilizes a series of electrical discharges to meticulously remove material from graphite. Renowned for its ability to produce highly precise and intricate shapes, EDM is a preferred method in the creation of molds and dies used in plastic injection molding. This process ensures exceptional accuracy and detail, making it indispensable in industries where precision and complexity are paramount.

How Do You Choose the Right Graphite Machining Process?
Selecting the appropriate machining process depends on several factors, such as:
- Part geometry and complexity: Intricate components may require EDM or multi-axis CNC machining.
- Surface finish requirements: Grinding is preferred for ultra-smooth surfaces, while milling offers versatility for general shaping.
- Production volume: High-volume runs often leverage automated CNC machines and standardized tooling.
- Required tolerances: Tight tolerances may necessitate specialized tooling or secondary finishing steps.
If you’re unsure which method is best for your project, consult with a knowledgeable graphite machining company for expert guidance.
Negatives of Graphite Machining Limitations
Despite its usefulness, graphite has several limitations. Its brittleness makes it susceptible to chipping and cracking during machining. Traditional machining techniques like milling, turning, and drilling not only produce substantial dust but also require frequent tool changes. This dust can be hazardous to health if inhaled, and its disposal, along with the potential release of graphite dust into the environment, raises significant concerns. Advanced machining methods such as electrical discharge machining (EDM) provide highly precise and intricate shapes but come with higher costs and longer processing times.
Additionally, the abrasive nature of graphite can accelerate tool wear, increasing operating costs and necessitating frequent tool replacements or maintenance. Environmental and workplace safety regulations must also be strictly followed to mitigate the impact of graphite dust and ensure a safe working environment. Companies evaluating graphite machining should weigh these limitations against their application needs, considering factors such as cost, turnaround time, and available safety measures.
Common user questions:
– How do I minimize graphite dust during machining?
– What are the best practices for tool maintenance with graphite?
– How do material limitations affect the lifespan of graphite components?
Graphite Machining Benefits
Even with its limitations, graphite machining presents numerous advantages, making it a favored choice across various fields. Graphite’s remarkable stability and resistance to chemicals make it especially suitable for harsh environments. Its superior thermal and electrical conductivity enhances its utility, particularly in the creation of electronic components and heating elements. Moreover, graphite’s light weight and ability to be machined to very precise tolerances highlight its flexibility and wide-ranging applicability.
Key benefits of graphite machining include:
- High-Temperature Endurance: Graphite’s ability to retain structural integrity at extreme temperatures makes it invaluable for furnace components, heat shields, and aerospace parts.
- Non-Reactivity: Graphite does not react with most chemicals, making machined graphite parts ideal for acid tanks, chemical reactors, and labware.
- Customizability: CNC and EDM technologies enable the fabrication of intricate, custom-designed graphite products, from micro-scale semiconductor parts to large industrial dies.
- Reduced Weight: Compared to metals, graphite components help reduce machinery weight without sacrificing strength or functionality.
- Excellent Lubricity: Machined graphite’s natural lubricating properties reduce friction and wear in moving parts and bearings.
Considering switching from metal to graphite? Review your application’s requirements for heat, corrosion resistance, and weight reduction to evaluate if graphite machining is the right solution for your project.
Applications of Graphite Machining
Graphite machining, renowned for its exceptional benefits, finds applications in numerous industries, such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and manufacturing. In the aerospace industry, graphite machining is essential for fabricating rocket nozzles and satellite components due to graphite’s remarkable ability to endure extreme temperatures and harsh environments.
Automotive engineers harness graphite machining to create EDM electrodes and spark plugs, capitalizing on graphite’s superior electrical conductivity and resistance to chemical erosion. In the electronics sector, experts utilize graphite machining to develop semiconductor components and LCD screens, thanks to graphite’s outstanding thermal and electrical conductivity.
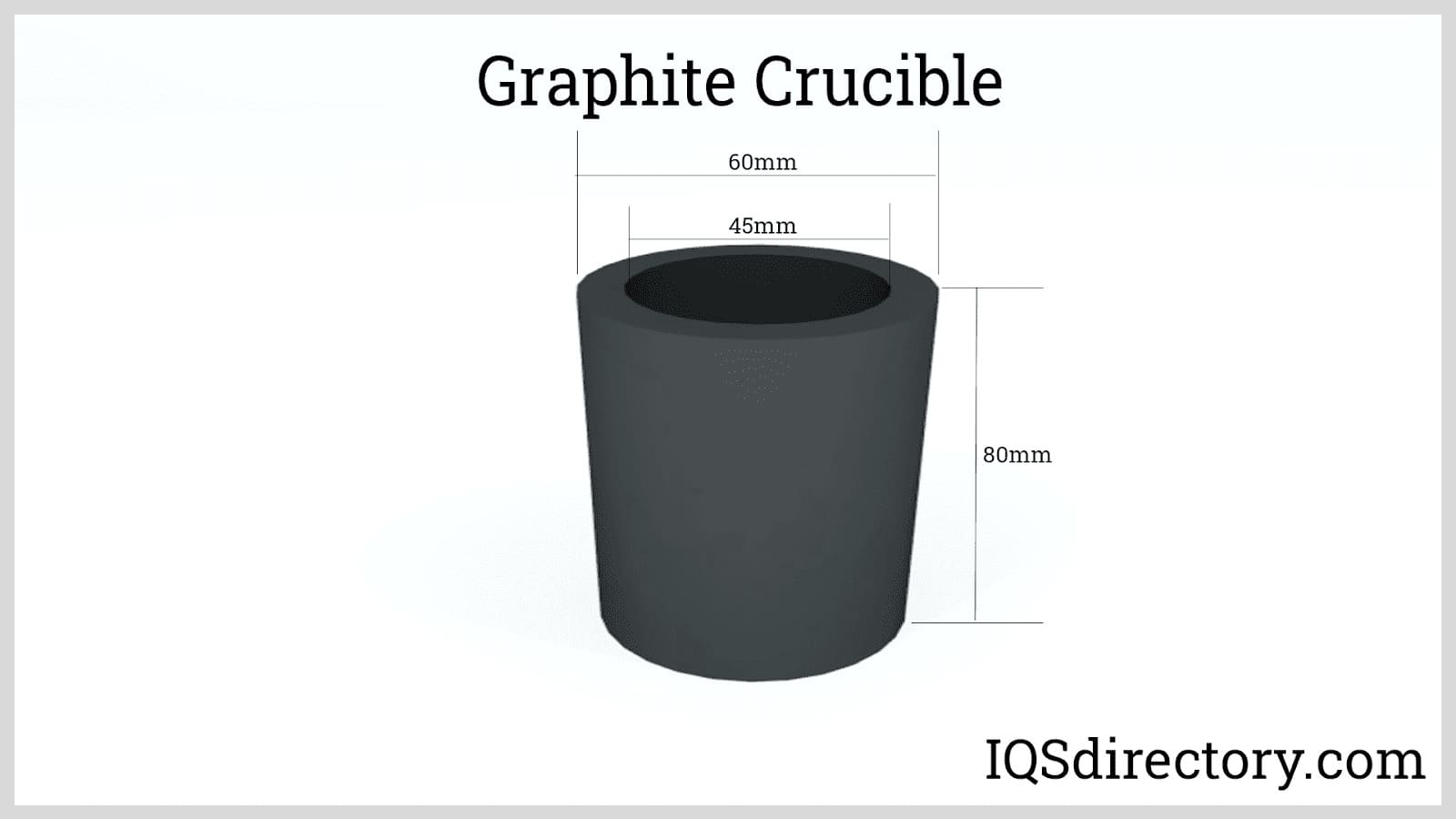
Manufacturers in the industry rely on graphite machining for producing molds for plastic injection and crucibles for metal casting, benefiting from graphite’s resilience to high temperatures and its resistance to chemical corrosion. These varied applications illustrate graphite machining’s vital role in enhancing technological advancements and industrial processes.

Industry-Specific Use Cases for Machined Graphite
- Aerospace: Thermal protection systems, rocket motor nozzles, and lightweight satellite structures.
- Automotive: EDM electrodes, spark plug components, lubrication systems, and brake linings.
- Electronics: Semiconductor manufacturing, heat sinks, and circuit board production.
- Metallurgy: Crucibles, casting molds, furnace linings, and continuous casting dies.
- Renewable Energy: Fuel cell plates, battery components, and solar panel manufacturing fixtures.
- Chemical Processing: Acid-resistant pump parts, seals, and gaskets.
Are you searching for graphite machining services for a specific industry or application? Explore our directory of graphite machining companies to find a provider that matches your sector and requirements.
How to Select the Right Grade of Graphite Material
Choosing the correct grade of graphite is critical for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Graphite grades vary by density, grain size, purity, and hardness, directly impacting their suitability for different machining methods and end-use applications. Key graphite types include:
- Isostatic Graphite: Offers the highest degree of isotropy, fine grain, and excellent machinability, ideal for EDM electrodes and semiconductor tools.
- Extruded Graphite: Suitable for larger, structural parts like rods and tubes, offering good machinability at a lower cost.
- Molded Graphite: Used for crucibles and foundry applications due to its strength and durability under thermal stress.
- Vibrated Graphite: Economical and used in less demanding applications such as heat exchangers and chemical processing equipment.
When evaluating graphite materials, ask suppliers about grain size, porosity, compressive strength, and compatibility with your intended machining process and operational environment.
Choosing the Correct Graphite Machining Company
To achieve optimal results when selecting a graphite machining company, utilize our directory to compare various businesses. Each company’s profile page details their expertise and capabilities, and includes a contact form for inquiries or quotes. Our proprietary website previewer allows you to swiftly understand each company’s specializations. Finally, use our streamlined RFQ form to reach out to multiple companies simultaneously.
Buyer’s Guide: What to Look for in a Graphite Machining Service
- Technical Expertise: Does the company have experience with your industry and application type?
- Machinery and Capabilities: What equipment do they use (CNC, EDM, custom tooling) and what are their quality standards?
- Material Sourcing: Can they source high-purity, application-specific graphite grades?
- Lead Times and Scalability: Are they equipped to handle prototype through high-volume production runs?
- Certifications: Do they hold relevant ISO or industry certifications for quality management and traceability?
- Customer Support: Will they assist with design, prototyping, and post-production support?
Ready to compare graphite machining companies? Browse our comprehensive directory or use our RFQ tool to request competitive quotes from multiple providers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Graphite Machining
- How does graphite machining compare to metal machining?
Graphite machining typically produces less tool wear due to its lubricity, but graphite’s brittleness requires more delicate handling and dust management. Metal machining often relies on coolant, while graphite machining is usually performed dry. - What are the environmental and health considerations?
Proper dust collection systems are essential to protect operator health and prevent graphite dust from contaminating the environment. Always comply with OSHA and local regulations. - What tolerances can be achieved with CNC graphite machining?
Tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm are achievable, depending on part geometry and machine precision. - Is custom graphite machining expensive?
Costs depend on part complexity, graphite grade, required tolerances, and production volume. High-precision, low-volume parts using premium grades may be more expensive, but bulk production and standardization reduce per-unit costs. - Can graphite machining be used for prototyping?
Yes, graphite’s machinability and moderate cost make it an excellent choice for rapid prototyping and short-run custom components.
Still have questions about graphite machining? Contact expert suppliers for guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Trends and Innovations in Graphite Machining
As technology evolves, graphite machining companies are adopting advanced manufacturing techniques to meet rising industry demands. Key trends include:
- Automation and Robotics: Automated CNC systems and robotic loading/unloading improve efficiency and consistency in high-volume graphite part production.
- Advanced Tooling: New tool coatings and geometries extend tool life and enhance performance with ultra-hard, fine-grain graphite materials.
- Digital Twin and CAD/CAM Integration: Digital modeling and simulation streamline the design-to-production workflow for complex graphite parts.
- Precision Metrology: Enhanced inspection and measurement systems ensure tighter quality controls, particularly for aerospace and semiconductor applications.
- Sustainable Practices: Companies are exploring recycling of graphite scrap and implementing eco-friendly dust collection and disposal systems.
Are you looking for a supplier who leverages the latest innovations in graphite machining? Ask prospective companies about their investment in technology, quality assurance, and sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion: The Value of Expert Graphite Machining
Graphite machining stands at the forefront of advanced manufacturing, offering unmatched versatility, precision, and performance for a wide range of industrial applications. Whether you require high-precision EDM electrodes, durable molds, or custom solutions for aerospace, automotive, electronics, or chemical processing, partnering with the right graphite machining company is critical for your project’s success.
Explore our graphite machining company directory to find experienced suppliers, read in-depth company profiles, and request quotes tailored to your needs. Harness the benefits of expertly machined graphite parts—precision, reliability, and innovation for the challenges of tomorrow’s industries.
What is graphite machining?
Graphite machining is the precision manufacturing process of shaping, cutting, and finishing graphite materials into desired components or products using specialized equipment. This process leverages graphite’s thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and machinability to produce parts for demanding industrial applications such as molds, electrodes, dies, and crucibles.
What are the main benefits of graphite machining over other materials?
Graphite machining offers high-temperature endurance, excellent chemical resistance, customizability, weight reduction, superior thermal and electrical conductivity, and natural lubricity, making it a favored choice for aerospace, electronics, and chemical processing applications compared to metals and other materials.
What equipment and tools are commonly used for graphite machining?
Graphite machining typically uses high-speed milling machines, CNC machines, EDM (electrical discharge machining) machines, diamond-coated tools, dust collection systems, and advanced inspection tools. These specialized machines and tools ensure precision, manage graphite’s brittleness, and minimize dust hazards during production.
What are the main limitations and challenges of graphite machining?
The main challenges of graphite machining include graphite’s brittleness, which causes chipping and cracking, significant dust generation, frequent tool wear, and the need for environmental and health safety measures due to hazardous graphite dust. Advanced techniques like EDM increase precision but may add cost and time.
How do you choose the right graphite grade for machining?
Selecting the right grade depends on parameters such as density, grain size, purity, and hardness. Isostatic graphite is best for fine, precise parts; extruded graphite is cost-effective for larger structural items; molded graphite handles thermal stress well; vibrated graphite fits less demanding uses. Discuss application requirements with suppliers to ensure optimal material selection.
What industries commonly use graphite machining and for which applications?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, metallurgy, renewable energy, and chemical processing use graphite machining for applications like thermal protection systems, EDM electrodes, semiconductor manufacturing, crucibles, fuel cell plates, and acid-resistant pump parts. Graphite’s properties make it invaluable in challenging and high-precision environments.
What factors should be considered when choosing a graphite machining company?
When selecting a graphite machining company, consider their technical expertise, type of machinery, quality certifications, material sourcing capabilities, lead times, scalability, and level of customer support offered. Assess if they have experience with your application and industry for best results.



 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services