GES-AGM
GES-AGMRequest A Quote
Parma, OhioAt GES-AGM, we pride ourselves on being at the forefront of graphite machining, leveraging over 50 years of expertise to deliver precision and innovation. Our advanced carbon and graphite materials, combined with our broad-based solutions, empower us and our customers to grow and evolve continuously. Throughout our history, we have always embraced challenges, and we eagerly anticipate tackling the opportunities and obstacles of both the present and future. Our commitment to excellence in graphite machining ensures that we remain leaders in the industry, providing unparalleled quality and service to our clients.
Leading Machined Graphite Companies
More Machined Graphite Companies
Additional Categories: Steel Service Centers, Storage Racks, Tape Suppliers, Test Chamber





 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
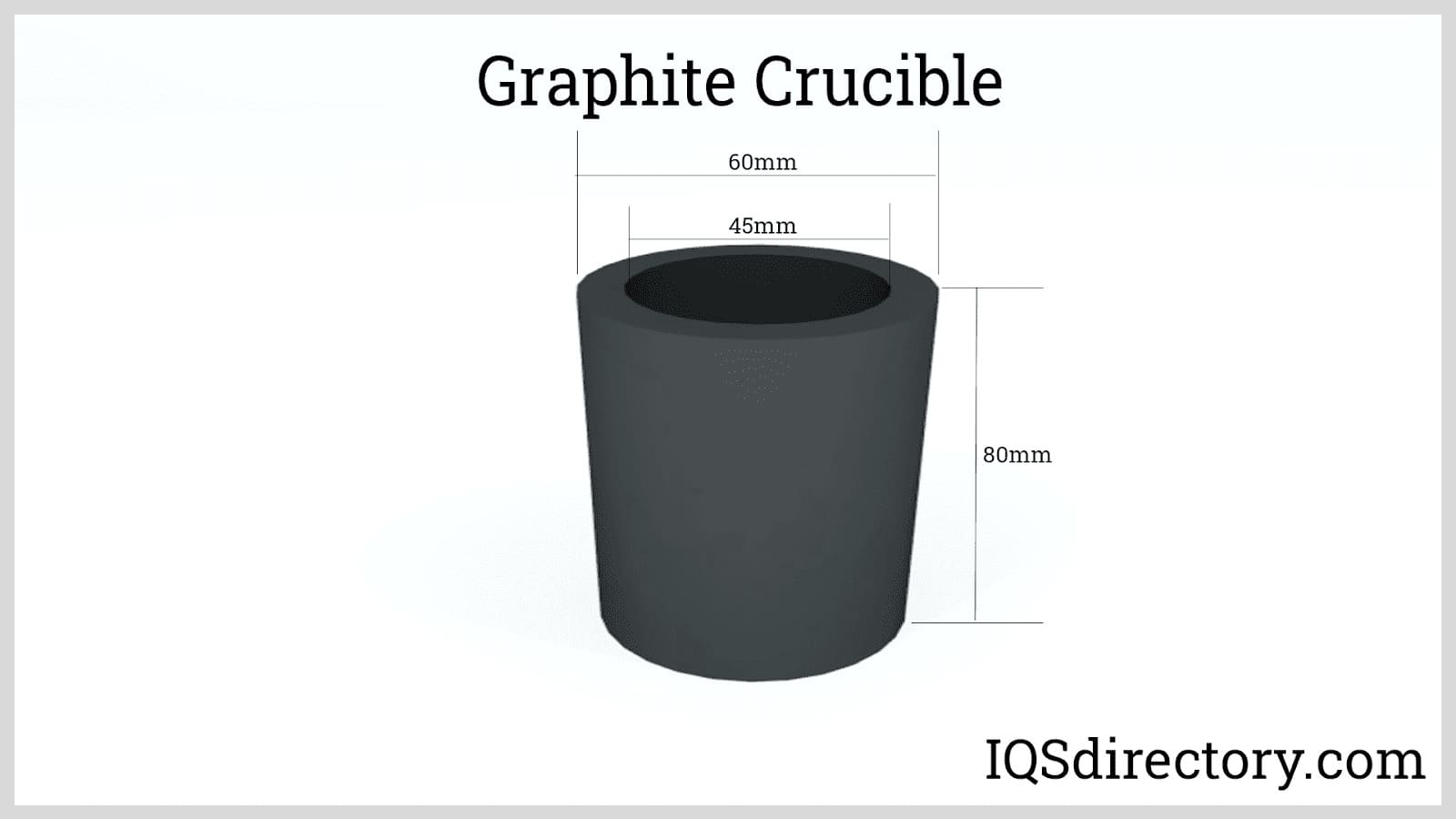
Glass Graphite
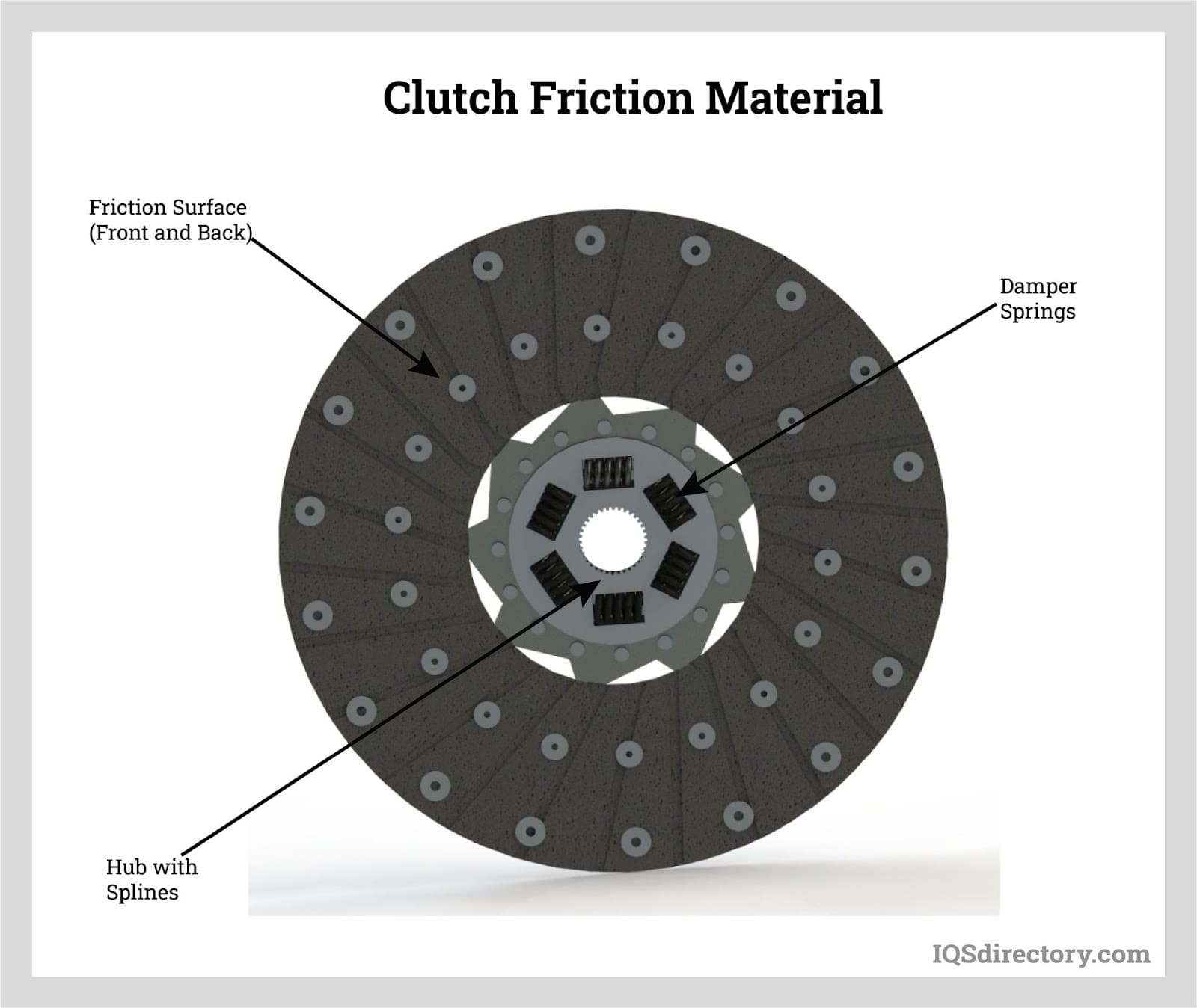
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services