Graphite is a crystalline form of carbon made with layered graphene. Graphite is the most stable type of carbon in nature under normal conditions. In 1989, 300 kton of natural and synthetic graphite were used in electrodes, lubricants, and pencils. At high temperatures and pressures, it transforms into a diamond. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity. Read More…
At Weaver Industries we specialize in manufacturing machined graphite parts and products. Our goal is to ensure that our customers get the right tools for their applications. We are leaders in the industry for our graphite machining processes which include recycling and reclaiming machined electrodes. Custom molded urethane and high quality carbon graphite are only a few of our other...

At Amsted, we specialize in precision graphite machining, delivering advanced solutions that meet the exacting standards of modern industries. Our team brings together decades of expertise and state-of-the-art technology to produce high-performance graphite components with superior accuracy, consistency, and surface quality.
SGL Carbon Group is the world's largest manufacturer of carbon and graphite, a leading provider of graphite specialties and the only company in the world to master all related manufacturing processes. We serve many industries with graphite materials, system solutions and graphite design.

More Graphite Product Companies

Graphite minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Graphite often develops when carbon is exposed to high pressure and temperatures in the earth's crust. Graphite can also be a naturally occurring type of crystalline carbon. Typically, graphite is oily and soft, cleaves easily under little pressure, and has low specific gravity. The hue of this mineral is black or grayish. It can resist extremely hot or cold temperatures and is a great conductor of electricity or heat. Another noteworthy feature is this mineral's ability to be chemically inert or unaffected by various chemicals and acids.
There are significant amounts of graphite in its natural state throughout the planet. Nevertheless, depending on the mineral's source, it is typically categorized into three forms: flake, crystalline, and amorphous. Graphite may be frequently utilized in numerous household products, in everything from tennis rackets to pencils. In addition, its peculiar chemical characteristics and relatively low cost of production make it a good choice as a lubricant for various industrial uses.
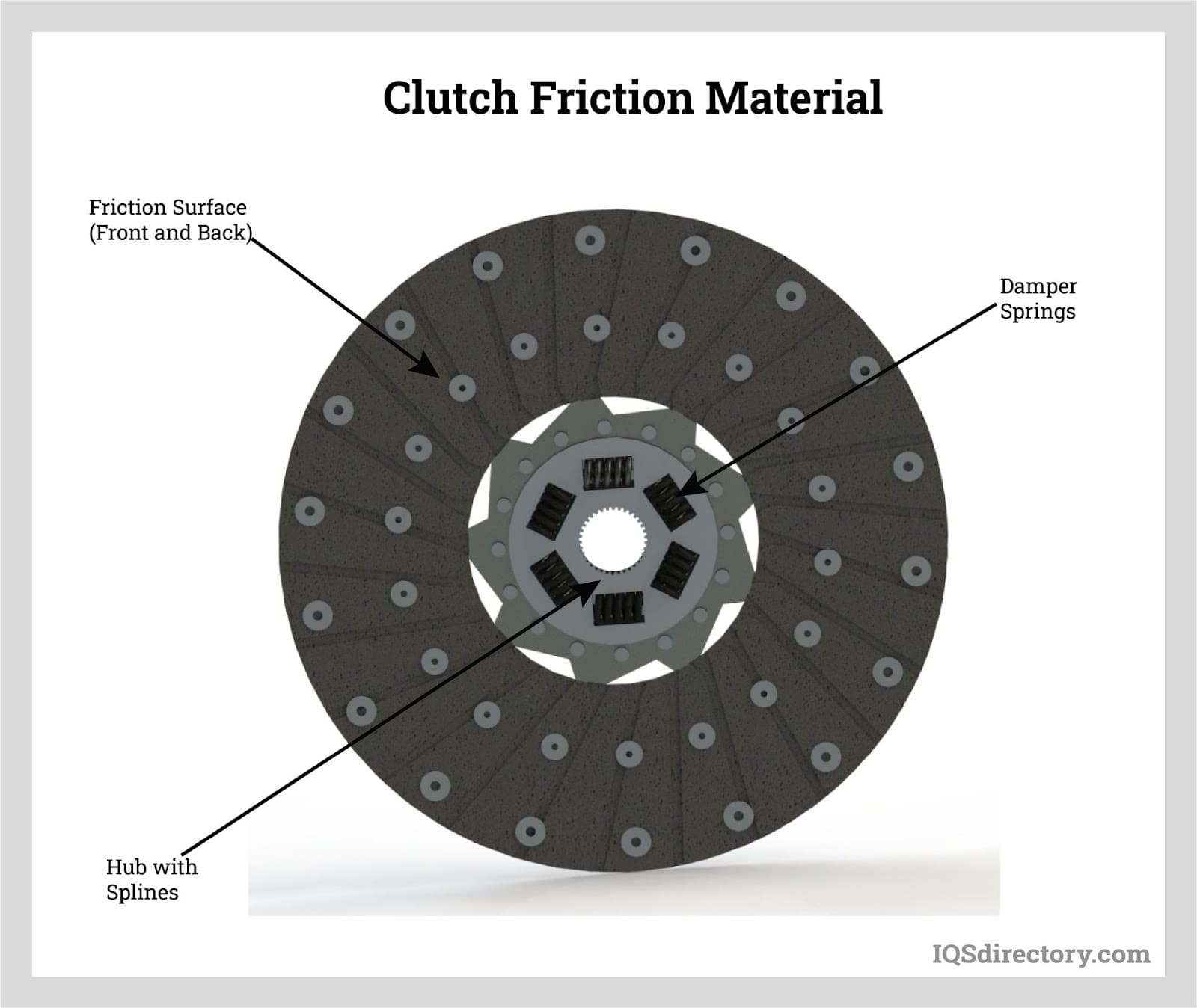
Types of Graphite Products
Graphite in Bearings
The purpose of bearings is to lessen friction between two surfaces. Since they are in contact with another moving part, they support a load. Due to its extended service life, self-lubricating properties, and resistance to severe environments, graphite is perfect for bearings.

Vane Construction
Blades are fastened to revolving wheels to push or be propelled by wind or water. Graphite is the ideal material for creating vanes due to its durability, strength, and resistance to water absorption.
Graphite Lubrication Blocks
Where wet lubricants cannot be utilized, lubrication blocks are employed. Most of their applications are in rotating machinery such as trunnion rolls, riding rings, tires, and insert seals. They constantly come into contact with the rolling surface due to their weight, leaving a thin graphite coating behind. The primary reasons graphite is used to lubricate blocks are its resistance to wear and long service life.

Low Porosity Graphite Brushes
Electric motor current is carried through square graphite brushes. They enable a consistent current transfer between commutator segments and protect them from wear. Pitch or resin is used as a binding agent while creating natural or manufactured graphite. Due to their high density and low porosity, graphite brushes won't become contaminated by the environment.
Graphite Anodes in Cathodic Protection Systems
Systems for cathodic protection employ graphite anodes. They function as an electrode in a mercury cell that generates chlorine. An electrical current starts as soon as the anode is put into a mercury pool cathode of an ignitron because the anode is an electron collector. In addition, an electrolytic cell's anodes have a positive polarity, which is where oxidation occurs. Due to its low cost, superior conductivity, and chemical inertness, graphite is the perfect material for cathodic protection.
Nuclear Graphite Cores
Graphite is a core and moderator material in high-temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactors. A nuclear reactor's graphite blocks are a safety precaution to keep the reactor running. Reactor cores are 1400 tons in weight, 32 feet (10 meters) in height, and 32 feet (10 meters) in diameter. Uranium fuel and control rods are introduced through passageways in the reactor's graphite core. The use of graphite bricks provides a structure for CO2 gas to flow through as it eliminates heat from the fuel, acts as a moderator, and slows down neutrons to assist in maintaining the nuclear reaction. The lifespan of the reactor is dependent on how the graphite matures.
Graphite Fluxing Tubes
To add fluxing gasses and purge hydrogen, aluminum oxide, and other materials from molten aluminum, fluxing tubes are used in aluminum applications for transfer ladles, melting furnaces, and holding furnaces. Thermal stress and corrosion are both resistant to graphite fluxing tubes. They are created by treating different grades of anti-oxidant-treated graphite. Fluxing tubes are available in various diameters or can be specially made to match any application because not all aluminum processing operations are identical.
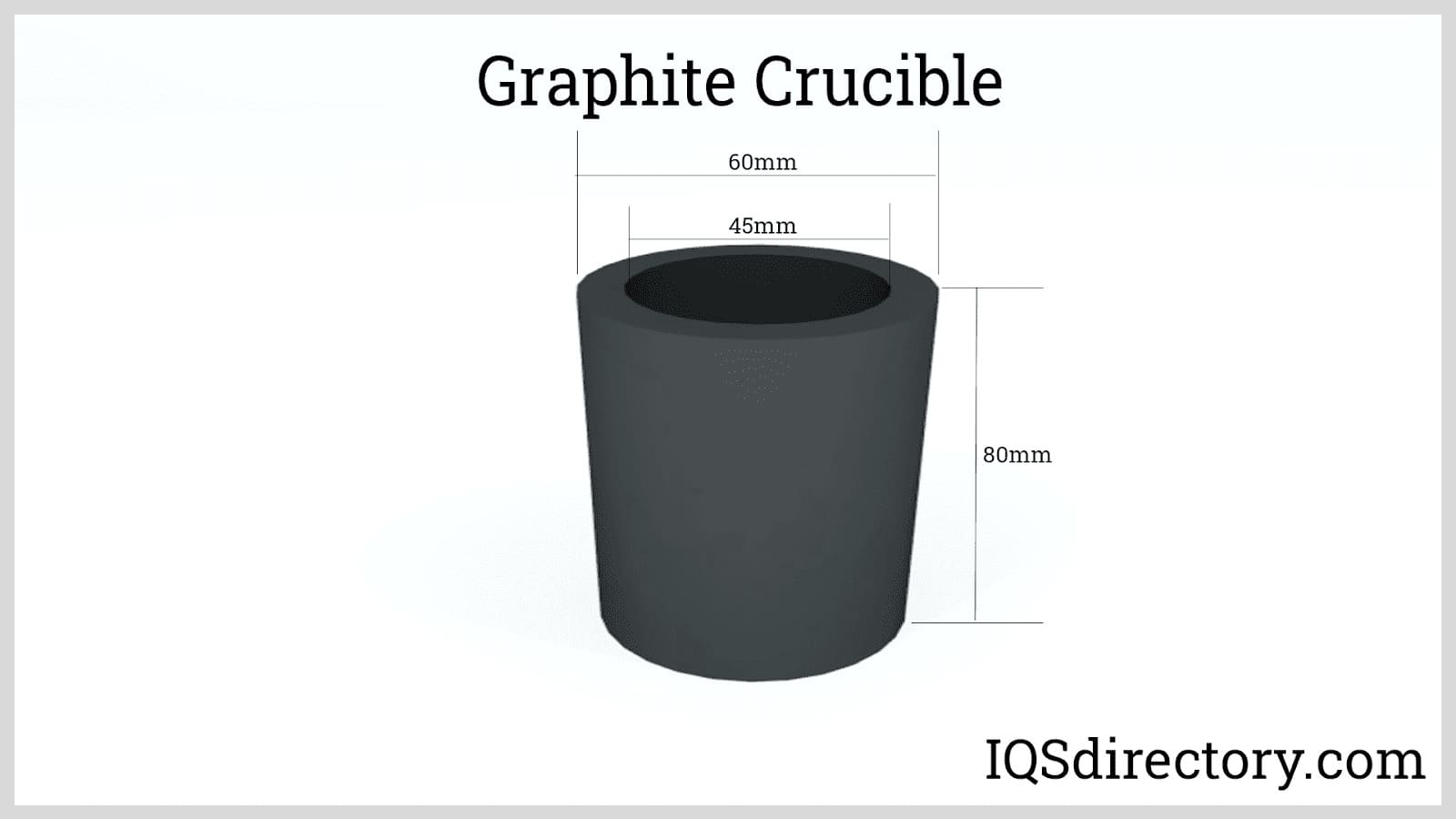
Graphite Crucibles for Material Melting
To refine precious and base metals, graphite crucibles melt materials at temperatures up to 2912 °F (1600° C). They are utilized in all production processes involving melting and casting. The materials used to create graphite crucibles enable processing of several metals with various melting points. Graphite crucibles come in various shapes to suit the requirements of the process because they are used in various applications.
For example, graphite crucibles are less expensive than copper, platinum, quartz, and porcelain crucibles and are available in barrel, cylinder, and cone shapes. In addition, graphite material can be used in melting furnaces since it is temperature resistant and chemically inert.
Choosing the Right Graphite Products Supplier
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing graphite products from a graphite products supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of graphite products suppliers. Each graphite products supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each graphite products supplier’s business website using our proprietary website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple graphite products suppliers with the same form.






 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services