The physical characteristics of superior thermal conductivity, strength, durability and shape and structure maintenance at absurdly high temperatures are a few of the reasons graphite is so popular. Due to the material’s low heat sensitivity, machined graphite tubes are often used in furnaces and heating components. Read More…
At Weaver Industries we specialize in manufacturing machined graphite parts and products. Our goal is to ensure that our customers get the right tools for their applications. We are leaders in the industry for our graphite machining processes which include recycling and reclaiming machined electrodes. Custom molded urethane and high quality carbon graphite are only a few of our other...

At Amsted, we specialize in precision graphite machining, delivering advanced solutions that meet the exacting standards of modern industries. Our team brings together decades of expertise and state-of-the-art technology to produce high-performance graphite components with superior accuracy, consistency, and surface quality.
SGL Carbon Group is the world's largest manufacturer of carbon and graphite, a leading provider of graphite specialties and the only company in the world to master all related manufacturing processes. We serve many industries with graphite materials, system solutions and graphite design.

More Graphite Tube Companies
Graphite tubes are renowned for their exceptional performance in high-temperature, corrosive, and demanding industrial environments. These tubes, made from high-purity graphite, offer unique properties such as superior thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and chemical resistance. This makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications, from degassing shafts and impellers to fluxing and injection tubes in various industrial processes.
Why choose graphite tubes? When evaluating materials for high-temperature operations or corrosive environments, graphite stands out due to its ability to maintain dimensional stability and mechanical integrity even at temperatures exceeding 5000°F (2760°C). In consumer and recreational products, carbon graphite tubes are valued for their lightweight strength—ideal for kite frames, tent supports, kayak riggers, handles, and fishing rods. Thanks to their outstanding corrosion resistance and thermal shock resilience, graphite tubes are frequently the first choice for equipment and components exposed to extreme conditions.
Graphite Tube Forming Process
The graphite tube manufacturing process is a highly specialized field within advanced materials engineering. Machining graphite to create tubes can involve several techniques: extrusion, compression molding, and isostatic pressing. Each production method results in unique graphite grades, tailored for specific applications and performance requirements. For example, extruded or pressed graphite is typically used in medium-duty industrial operations, while isostatically pressed graphite offers superior particle fineness and smoother finishes—crucial for high-precision applications.
Graphite rods and plates made from isostatically pressed graphite are characterized by their fine grain structure and smooth surfaces, making them ideal for industries where dimensional accuracy and surface quality are critical. Customization is straightforward: manufacturers can produce graphite tubes in virtually any length, diameter, wall thickness, or flexibility, ensuring a perfect fit for your project or process requirements.
Unlike metals, graphite’s mechanical strength actually improves as operating temperatures increase, making it uniquely suited for high-temperature furnace tubes and heat exchanger applications. Its resistance to degradation from normal wear and tear means reduced maintenance and longer service life, reducing total cost of ownership over time.
Coating graphite tubes is an optional but often advantageous step. Applying protective coatings, such as siloxane, significantly extends tube life by increasing resistance to oxidation, even during prolonged high-temperature use. In some cases, metallic graphite blends may be selected to enhance electrical conductivity or mechanical strength. For example, copper graphite may be preferred in electrical discharge machining (EDM) electrodes or other applications where both electrical and thermal conductivity are essential, though it is typically more expensive than pure graphite.

Types of Graphite Tubes
Understanding the different types of graphite tubes is key to selecting the right solution for your application. Each type offers a distinct balance of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is a detailed overview of the most common graphite tube variants:
Carbon-Bonded Graphite Tubes
Carbon-bonded graphite tubes are manufactured by combining extruded graphite flour, lubricants, and resin, then subjecting them to heat treatments up to 1200°C. This process creates a composite tube containing both graphite and amorphous carbons. The lower production temperature results in energy savings and reduced wear on manufacturing equipment.

These tubes are typically more affordable than fully graphitized tubes and offer a porosity of 8–10%. When subjected to a phenolic resin bake cycle, they become virtually impervious—an important factor for fluid handling and chemical processing. Carbon-bonded tubes also demonstrate superior thermal properties compared to resin-bonded pipelines and are valued for their enhanced resistance to thermal and mechanical shock.
Resin-Bonded Graphite Tubes
Resin-bonded graphite tubes are created by blending graphite powder with a resin binder, then extruding the mixture to the desired length and shape. The high resin content yields a non-porous tube that does not require additional impregnation, streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing costs.

The primary advantage of resin graphite tubes is cost—they can be up to 50% more economical than partially or fully graphitized alternatives. However, their resistance to corrosion and high temperatures is limited. In harsh, high-temperature environments, resin-bonded tubes may degrade more rapidly, making them better suited for low- to medium-duty applications where extreme operating conditions are not a concern.
Fully Graphitized Tubes
Fully graphitized graphite tubes undergo an advanced heat treatment process in a graphitizing furnace at approximately 2800°C. This process eliminates all amorphous carbon, resulting in a tube with exceptional thermal and electrical properties. Fully graphitized tubes exhibit the lowest thermal expansion, outstanding fatigue tolerance, superior durability, flexibility, and the highest levels of thermal conductivity among all graphite tube types.
These tubes are ideal for precision demanding industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, high-temperature furnaces, and advanced research laboratories. Their unique properties also make them the preferred choice for heat exchangers, analytical equipment, and certain aerospace and energy applications.
Pyrolytic Graphite Tubes
Pyrolytic graphite tubes are produced via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), using purified methane or other hydrocarbon gases. The resulting coated surface is virtually non-porous and extremely pure, often exceeding 99.999% carbon purity (impurities <10ppm). The standard membrane thickness ranges from 30 to 50 micrometers.
The main advantages of pyrolytic graphite tubes are their ultra-high purity, excellent strength, and virtually zero porosity. These characteristics make them ideal for analytical instrumentation, semiconductor processing, and other applications where contamination control is paramount. If your project requires ultra-high purity graphite, pyrolytic tubes represent the leading-edge solution.
Applications of Graphite Tubes
What are the main uses of graphite tubes? Graphite tubes serve as critical components across a wide spectrum of industries due to their unique combination of chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties. Some of the most common and high-value applications include:
- Graphite tube furnaces: Used in analytical laboratories for atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), providing stable, high-temperature environments for precise sample analysis. Selecting the right graphite tube is essential based on the target element and matrix composition.
- Corrosion-resistant tubing: Employed in chemical processing plants and acid pickling lines, where they handle aggressive fluids and gases without degradation.
- Heat exchangers: Graphite tubes excel in both shell-and-tube and block heat exchanger designs, efficiently transferring heat in corrosive or ultra-high temperature service conditions.
- Metal casting and foundry: Used in degassing shafts, fluxing tubes, and injection tubes for molten metals, ensuring clean and controlled processing of aluminum, copper, steel, and other alloys.
- Energy storage and batteries: Graphite tubes are integral in advanced lithium-ion battery designs and supercapacitors due to their excellent electrical conductivity and inertness.
- Research and development: Utilized in high-temperature furnaces, vacuum systems, and custom lab equipment for scientific research and new material synthesis.
- Environmental analysis: Used for sampling and analyzing environmental and biosamples—such as seawater and industrial waste—where chemical resistance and purity are crucial.
- Electrochemical cells and fuel cells: Serve as flow field plates, current collectors, or structural supports in electrochemical and energy conversion systems.
Industries relying on graphite tubes include:
- Chemical processing and manufacturing
- Metallurgy and metal refining
- Pharmaceutical production and lab analysis
- Electroplating and surface finishing
- Printing and paper manufacturing
- Environmental protection and pollution control
- Energy production and storage (batteries, fuel cells)
- Semiconductor and electronics manufacturing
- Aerospace and defense industries
- Automotive and transportation technology
Other Notable Graphite Tube Applications
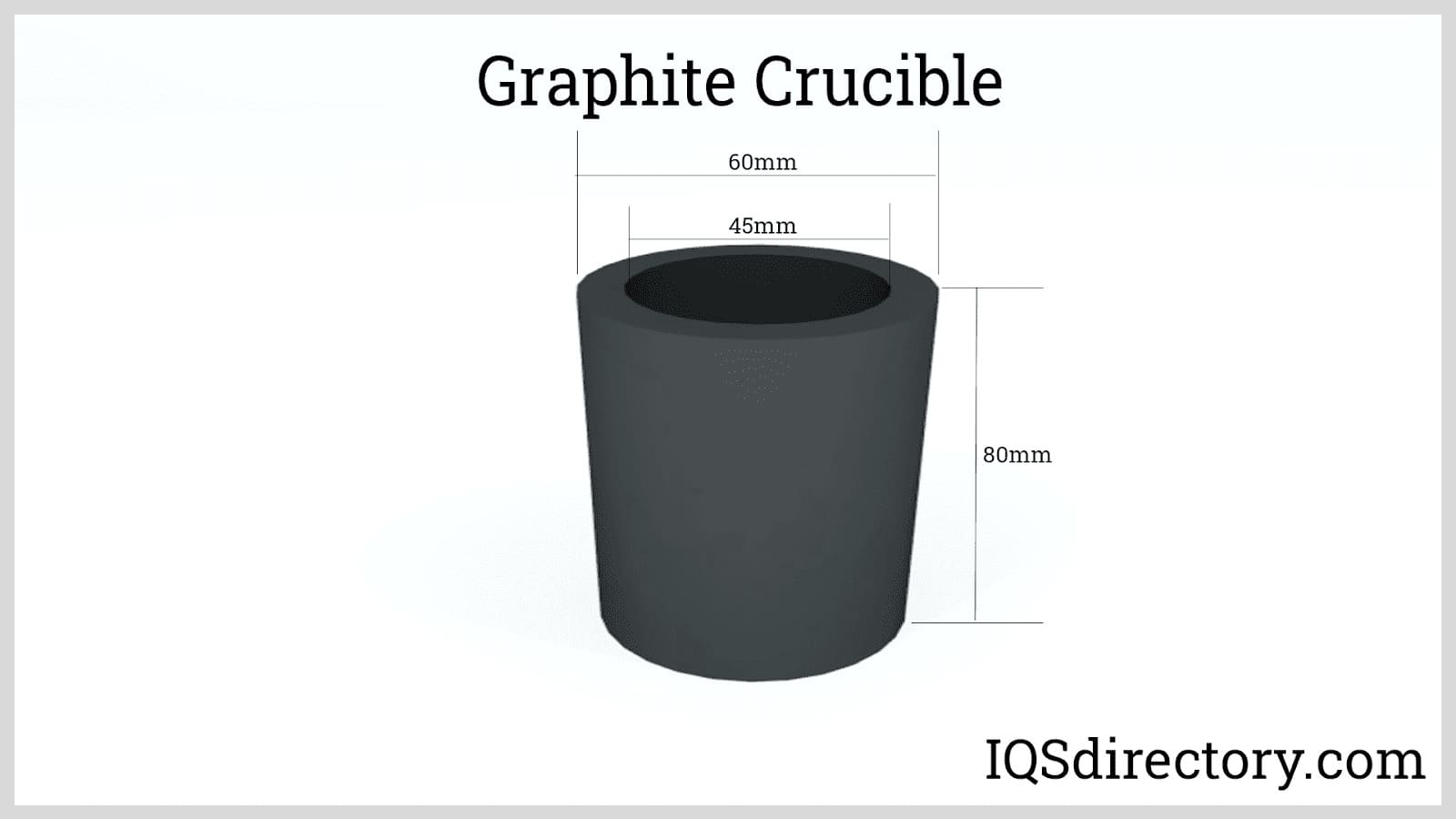
- Extreme heat and harsh environment components: furnace liners, crucibles, heating elements.
- Consumer products: lightweight sporting goods (e.g., kite, tent, and fishing rod frames), graphite pencils, golf club shafts, and recreational equipment.
- Advanced manufacturing: EDM electrodes, molds for glass and metal forming, and high-purity components for semiconductor processing.
- Steel production and continuous casting: Graphite tubes are used for guiding molten steel and as part of the casting process due to their thermal shock resistance.
- Lithium-ion batteries and energy storage: Utilized as both current collectors and structural supports in battery cells.

Benefits of Graphite Tubes
Why are graphite tubes the preferred choice for industrial applications? The advantages of graphite tubes extend well beyond their basic physical properties. Here’s why engineers, plant managers, and product designers consistently select graphite tubing for demanding applications:
- Exceptional acid and chemical resistance: Graphite tubes remain stable and inert even when exposed to strong acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments.
- Superior structural strength and impact resistance: Despite being lightweight, graphite tubes offer impressive mechanical strength and can withstand mechanical shocks and vibrations.
- High thermal conductivity and shock resistance: Graphite efficiently transfers heat and can handle rapid temperature changes without cracking or deforming, essential for heat exchangers and furnace components.
- Extended service life and ease of maintenance: Graphite tubes are long-lasting and require minimal upkeep, reducing overall maintenance costs and process downtime.
- High volume utilization and design flexibility: Easily machined to precise tolerances and customizable for a wide range of configurations and sizes.
- Environmentally friendly and recyclable: Graphite is a naturally occurring material that can often be recycled or repurposed at the end of its service life.
Additional Advantages of Graphite Tubes
- Unique strength-temperature relationship: When heated from ambient to 2,000°C, graphite actually becomes stronger due to reduced internal stresses. This allows for lighter, more compact designs and larger batch processing in industrial operations.
- Chemical inertness: Mechanical carbon-graphite grades are unaffected by most acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making them ideal for chemical pumps, valves, and food processing machinery where contamination and corrosion must be avoided.
- Thermal management: Graphite’s high thermal conductivity draws heat away from friction points (such as seal faces), which is essential in rotating equipment, bearings, and high-speed industrial machinery.
- Customizable porosity and impregnation: Graphite tubes can be engineered with different degrees of porosity or impregnated with resins/metals for enhanced impermeability and tailored performance. This versatility supports a vast array of industrial and research applications.
- Non-magnetic and electrically conductive: Graphite is ideal for electrical and electronic applications where magnetic interference must be minimized and reliable conductivity is needed.
Curious about the best graphite tube type for your needs?
Explore how different grades, manufacturing processes, and coatings can optimize performance for your specific project. Consider these questions:
- What temperature range will the tube be exposed to?
- Will it handle corrosive chemicals or aggressive fluids?
- Is electrical conductivity or thermal conductivity a primary concern?
- Does the application require ultra-high purity or low porosity?
- Are there constraints on size, shape, or mechanical load?
Choosing the Correct Graphite Tube Supplier
How do you select the best graphite tube manufacturer or supplier? Choosing a trustworthy and experienced graphite tube supplier is critical to ensuring product quality, performance, and value. Here are key decision factors to consider during your supplier evaluation process:
- Technical expertise: Does the supplier have a proven track record in custom graphite machining, tube forming, and advanced material solutions?
- Material sourcing and quality control: Are raw materials high-purity and traceable? Does the supplier provide material certifications and detailed quality assurance documentation?
- Customization capability: Can they engineer graphite tubes to your exact specifications—length, diameter, wall thickness, surface finish, and porosity?
- Turnaround time and logistics: Is the supplier responsive and able to meet your deadlines for prototypes, production runs, or emergency replacements?
- Application support and engineering guidance: Do they offer consultation to help you select the right graphite grade, coating, or impregnation for your application?
- Cost-effectiveness: Are their prices competitive, and do they offer value-added services such as machining, coating, or assembly?
- Customer reviews and references: Can the supplier demonstrate a history of satisfied clients in your industry sector?
To ensure the most positive outcome when purchasing graphite tubes from a reputable supplier, compare several companies using our comprehensive directory of graphite tube suppliers. Each supplier profile includes details on their expertise, manufacturing capabilities, and product offerings, along with a direct contact form for information requests or quotes. Review supplier websites using our proprietary previewer to quickly assess their specialties, and leverage our easy-to-use RFQ form to reach multiple graphite tube manufacturers and distributors simultaneously.
Ready to source graphite tubes for your next project?
Browse our directory, compare suppliers, and request custom quotes to find the ideal graphite tube solution for your application. Whether you need bulk quantities for industrial production or precision-cut tubes for laboratory use, our network connects you with industry-leading suppliers and expert support every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions About Graphite Tubes
- What is the lifespan of a graphite tube in a furnace or heat exchanger?
Lifespan depends on the specific grade, operating temperature, chemical exposure, and maintenance schedule. High-quality, fully graphitized tubes can last several years in continuous service, while resin-bonded tubes may need more frequent replacement in harsh environments. - How do I specify the right graphite tube for my application?
Review your process requirements (temperature, chemical exposure, mechanical load, conductivity needs, etc.), then consult with a supplier or materials engineer to select the optimal grade, dimensions, and coating options. - Can graphite tubes be machined to tight tolerances?
Yes. Graphite’s machinability allows for the production of tubes with precise internal and external diameters, surface finishes, and even complex geometries. - Are graphite tubes recyclable?
Many graphite tubes can be recycled or repurposed depending on contamination and end-of-life condition, supporting sustainability goals in manufacturing and process industries. - What are the delivery times for custom graphite tubes?
Lead times vary by supplier, complexity, and order volume. For urgent requirements, look for suppliers with rapid prototyping or expedited manufacturing capabilities.
Still have questions about graphite tubes, custom graphite machining, or sourcing strategies?
Contact our expert team or explore our resource library for in-depth guides, technical articles, and product selection tools.






 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services